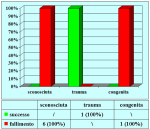
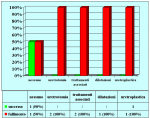
L’intervento denominato “anastomosi termino-terminale” consiste nel sezionare completamente l’uretra nel punto in cui è presente la stenosi, asportare il tessuto cicatriziale e suturare insieme i due monconi ripristinando la continuità del canale. Questo intervento è uno di primi interventi descritti per la riparazione delle stenosi uretrali.
|
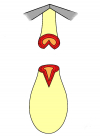
Figura 1 |
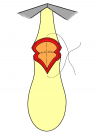
Figura 2 |
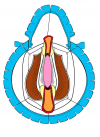
Figura 3 |
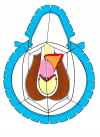
Figura 4 |
Fondamentalmente, esistono due tipi di anastomosi termino-terminale:
- Anastomosi termino-terminale. In questa procedura il canale uretrale viene completamente sezionato a livello della stenosi, il tessuto cicatriziale viene rimosso ed i due monconi uretrali vengono riavvicinati e suturati insieme (figure 1,2).
- Anastomosi termino-terminale con innesto di cute o mucosa orale. In questa procedura il canale uretrale viene completamente sezionato a livello della stenosi, il tessuto cicatriziale viene rimosso ed i due monconi uretrali vengono riavvicinati e suturati sopra un innesto di cute o mucosa orale (figure 3,4).
L’intervento chirurgico denominato anastomosi termino-terminale è indicato fondamentalmente nei seguenti casi:
- pazienti con stenosi traumatica dell’uretra bulbare, di lunghezza non superiore a 2 cm.
- pazienti già sottoposti, con esito negativo, ad intervento di uretroplastica che presentano una stenosi recidiva fibrosa ma non superiore a 2 cm di lunghezza.
Articolo n° 1
Barbagli G, Selli C, di Cello V, Mottola A.
A one-stage dorsal free-graft urethroplasty for bulbar urethral strictures.
Br J Urol. 1996 Dec;78(6):929-32
Articolo n° 2
Barbagli G, Selli C, Tosto A, Palminteri E.
Dorsal free graft urethroplasty
J Urol. 1996 Jan;155(1):123-6
Articolo n° 3
Barbagli G, Palminteri E, Rizzo M.
Dorsal onlay graft urethroplasty using penile skin or buccal mucosa in adult bulbourethral strictures.
J Urol. 1998 Oct;160(4):1307-9
Articolo n° 4
Barbagli G, Palminteri E, Lazzeri M, Guazzoni G, Turini D.
Long-term outcome of urethroplasty after failed urethrotomy versus primary repair
J Urol. 2001 Jun;165(6 Pt 1):1918-9
Articolo n° 5
Barbagli G, Palminteri E, Guazzoni G, Montorsi F, Turini D, Lazzeri M.
Interim outcomes of dorsal skin graft bulbar urethroplasty.
JUrol. Volume 172, Issue 4, Pages 1365-1367 (October 2004)
Articolo n° 6
Guido Barbagli, Giuseppe Morgia, Massimo Lazzeri
Dorsal Onlay Skin Graft Bulbar Urethroplasty: Long-Term Follow-Up
Eur. Urol. 2008,53:628 – 634
Barbagli G, Selli C, di Cello V, Mottola A.
A one-stage dorsal free-graft urethroplasty for bulbar urethral strictures.
Br J Urol. 1996 Dec;78(6):929-32
Articolo n° 2
Barbagli G, Selli C, Tosto A, Palminteri E.
Dorsal free graft urethroplasty
J Urol. 1996 Jan;155(1):123-6
Articolo n° 3
Barbagli G, Palminteri E, Rizzo M.
Dorsal onlay graft urethroplasty using penile skin or buccal mucosa in adult bulbourethral strictures.
J Urol. 1998 Oct;160(4):1307-9
Articolo n° 4
Barbagli G, Palminteri E, Lazzeri M, Guazzoni G, Turini D.
Long-term outcome of urethroplasty after failed urethrotomy versus primary repair
J Urol. 2001 Jun;165(6 Pt 1):1918-9
Articolo n° 5
Barbagli G, Palminteri E, Guazzoni G, Montorsi F, Turini D, Lazzeri M.
Interim outcomes of dorsal skin graft bulbar urethroplasty.
JUrol. Volume 172, Issue 4, Pages 1365-1367 (October 2004)
Articolo n° 6
Guido Barbagli, Giuseppe Morgia, Massimo Lazzeri
Dorsal Onlay Skin Graft Bulbar Urethroplasty: Long-Term Follow-Up
Eur. Urol. 2008,53:628 – 634
1. Domanda: Per questo tipo di intervento quale tipo di anestesia è previsto?
Risposta: Anestesia generale con intubazione oro-tracheale.
2. Domanda: Quante ore dura l’intervento?
Risposta: Circa due ore.
3. Domanda: Ci sono rischi per l’erezione, la fertilità e la continenza urinaria, dopo l’intervento?
Risposta: No
4. Domanda: Quanti sono i giorni di degenza in ospedale previsti per questo intervento?
Risposta: In genere il ricovero ospedaliero varia da 5 a 7 giorni.
5. Domanda: Per quanto tempo dovrò portare il catetere dopo l’intervento?
Risposta: Il catetere deve rimanere in sede per quattro settimane dopo l’intervento. Fino a quando non verrà effettuata la prima radiografia di controllo postoperatoria.
6. Domanda: Quali particolari limitazioni sono suggerite durante la convalescenza?
Risposta: Durante la convalescenza è suggerito l’uso di un antibiotico per via orale fino a che non viene rimosso il catetere. È suggerito di non effettuare lungi viaggi in auto, lavori pesanti, attività sessuale e sportiva.
7. Domanda: Quanto tempo dopo l’intervento potrò riprendere la mia attività lavorativa, sportiva e sessuale?
Risposta: Le attività lavorativa, sportiva e sessuale possono essere riprese gradualmente dopo circa 30 giorni dalla rimozione del catetere.
8. Domanda: Dopo l’intervento posso usare la bicicletta od il motorino?
Risposta: L’uso di bicicletta, motorino, cavallo, mezzi a sella in palestra sono sconsigliati.
9. Domanda: Quali cibi e bevande devo evitare dopo l’intervento?
Risposta: L’uso di birra, vini spumanti e gassati sono controindicati. Un uso esagerato di cioccolata, cacao, frutta secca, crostacei non è consigliato.
Risposta: Anestesia generale con intubazione oro-tracheale.
2. Domanda: Quante ore dura l’intervento?
Risposta: Circa due ore.
3. Domanda: Ci sono rischi per l’erezione, la fertilità e la continenza urinaria, dopo l’intervento?
Risposta: No
4. Domanda: Quanti sono i giorni di degenza in ospedale previsti per questo intervento?
Risposta: In genere il ricovero ospedaliero varia da 5 a 7 giorni.
5. Domanda: Per quanto tempo dovrò portare il catetere dopo l’intervento?
Risposta: Il catetere deve rimanere in sede per quattro settimane dopo l’intervento. Fino a quando non verrà effettuata la prima radiografia di controllo postoperatoria.
6. Domanda: Quali particolari limitazioni sono suggerite durante la convalescenza?
Risposta: Durante la convalescenza è suggerito l’uso di un antibiotico per via orale fino a che non viene rimosso il catetere. È suggerito di non effettuare lungi viaggi in auto, lavori pesanti, attività sessuale e sportiva.
7. Domanda: Quanto tempo dopo l’intervento potrò riprendere la mia attività lavorativa, sportiva e sessuale?
Risposta: Le attività lavorativa, sportiva e sessuale possono essere riprese gradualmente dopo circa 30 giorni dalla rimozione del catetere.
8. Domanda: Dopo l’intervento posso usare la bicicletta od il motorino?
Risposta: L’uso di bicicletta, motorino, cavallo, mezzi a sella in palestra sono sconsigliati.
9. Domanda: Quali cibi e bevande devo evitare dopo l’intervento?
Risposta: L’uso di birra, vini spumanti e gassati sono controindicati. Un uso esagerato di cioccolata, cacao, frutta secca, crostacei non è consigliato.
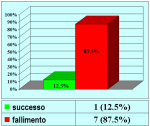
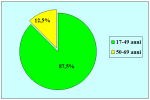
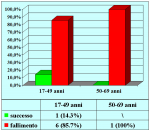
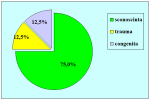
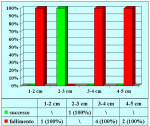
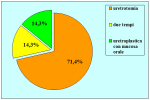
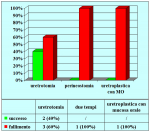
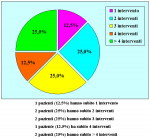
| Risultati aggiornati al 31 dicembre 2021 | |||

Tabella pazienti |
|||