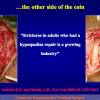
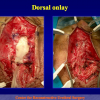
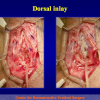
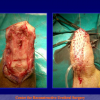
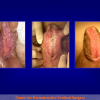
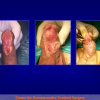
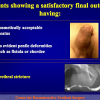
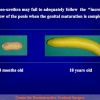
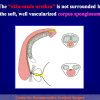
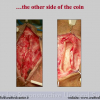
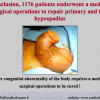
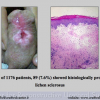
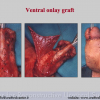
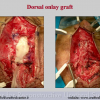
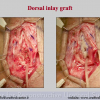
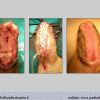
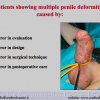
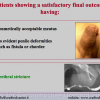
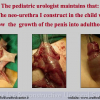
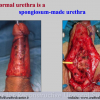
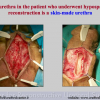
尿道下裂可由表现为三种情况:尿道开口位置异常,阴茎下弯,包皮发育异常或者包皮帽状堆积包裹背侧龟头。尿道下裂是最常见的阴茎先天性异常,在活婴中发生率为1/300。尿道下裂受多种病因影响:遗传易感性和内分泌紊乱。近年来研究表明在西方国家中尿道下裂的发生率逐步增高,第三世界国家和发展中国家的发病率甚至更高。
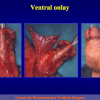
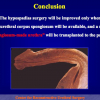
美国儿科协会建议在6至12个月行尿道下裂修复术。目前的治疗标准是门诊手术一期修复尿道下裂,改善阴茎外形,使患者可以站立排尿以及提高生育能力。
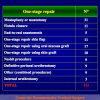
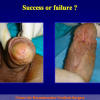
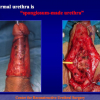
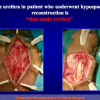
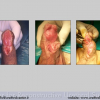
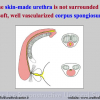
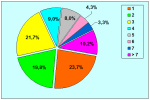
首次尿道下裂手术修复术后可能会造成一些术后并发症,需要二次手术矫正,如:瘘管,憩室,尿道口后移,阴茎下弯以及尿道狭窄。这些初次手术造成的问题可能是由于手术设计或操作失误,术后护理不当如感染、伤口裂开、尿液外渗、血肿、移植物的缺血坏死造成的。尿道下裂手术失败也可能在成功恢复阴茎功能和美观的许多年以后发生。矫正接受过尿道下裂修复术的手术操作较首次手术更为复杂,因为首次手术后会造成瘢痕增厚、固定,血供不足或阴茎显著缩短。对于首次尿道下裂手术失败或是需要再次手术的流行病学资料较少,可能是用于儿科泌尿医生随访时间较短,而在出现问题后已过去多年,由成人泌尿外科医生接手。
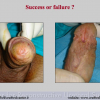
针对多次尿道下裂修复失败的患者的治疗仍然是一个难题,对于医保系统,全科医生,儿科医生,外科医生病人自己及其父母都是比较大的负担。这部分患者的治疗情况要比未接受治疗的患者更加棘手。
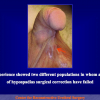
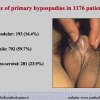
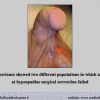
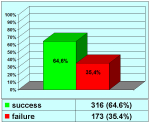
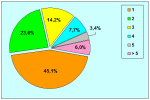
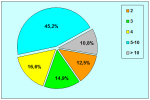
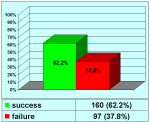
本中心经治的1510位患者中有14.7%的原发疾病为尿道狭窄。其中51%的转折首次手术的疗效不理想。阴茎狭窄患者中有近一半的患者是接受过尿道下裂修复术的。以上数据可能还不能完全估计成人人群中的实际情况。
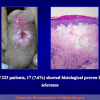
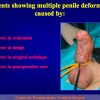
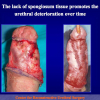
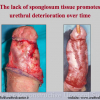
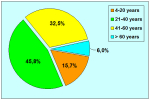
出现首次手术修复失败的人群大体分为两类:一部分患者是术后就出现了更加严重的阴茎畸形,瘘管,尿道下裂未完全矫正,阴茎下弯,阴茎或包皮外形难以接受。另一类患者是手术成功的改善了阴茎外形,矫正了尿道口位置,但由于尿道狭窄改善不佳而造成尿路梗阻的症状。这部分患者往往已经停止了小儿泌尿外科医生的随访多年,开始性生活后逐步出现越来越多的问题。部分先天海绵体缺如的患者术后恶化情况更快。这可能是由于新生的组织不能像正常组织一样适应成年以后阴茎反复勃起以及性交活动所带来的牵拉。阴茎海绵体在性生活过程中的作用与汽车的气囊在交通事故中所起的保护作用类似。
美国儿科协会建议在6至12个月行尿道下裂修复术。目前的治疗标准是门诊手术一期修复尿道下裂,改善阴茎外形,使患者可以站立排尿以及提高生育能力。
首次尿道下裂手术修复术后可能会造成一些术后并发症,需要二次手术矫正,如:瘘管,憩室,尿道口后移,阴茎下弯以及尿道狭窄。这些初次手术造成的问题可能是由于手术设计或操作失误,术后护理不当如感染、伤口裂开、尿液外渗、血肿、移植物的缺血坏死造成的。尿道下裂手术失败也可能在成功恢复阴茎功能和美观的许多年以后发生。矫正接受过尿道下裂修复术的手术操作较首次手术更为复杂,因为首次手术后会造成瘢痕增厚、固定,血供不足或阴茎显著缩短。对于首次尿道下裂手术失败或是需要再次手术的流行病学资料较少,可能是用于儿科泌尿医生随访时间较短,而在出现问题后已过去多年,由成人泌尿外科医生接手。
针对多次尿道下裂修复失败的患者的治疗仍然是一个难题,对于医保系统,全科医生,儿科医生,外科医生病人自己及其父母都是比较大的负担。这部分患者的治疗情况要比未接受治疗的患者更加棘手。
本中心经治的1510位患者中有14.7%的原发疾病为尿道狭窄。其中51%的转折首次手术的疗效不理想。阴茎狭窄患者中有近一半的患者是接受过尿道下裂修复术的。以上数据可能还不能完全估计成人人群中的实际情况。
出现首次手术修复失败的人群大体分为两类:一部分患者是术后就出现了更加严重的阴茎畸形,瘘管,尿道下裂未完全矫正,阴茎下弯,阴茎或包皮外形难以接受。另一类患者是手术成功的改善了阴茎外形,矫正了尿道口位置,但由于尿道狭窄改善不佳而造成尿路梗阻的症状。这部分患者往往已经停止了小儿泌尿外科医生的随访多年,开始性生活后逐步出现越来越多的问题。部分先天海绵体缺如的患者术后恶化情况更快。这可能是由于新生的组织不能像正常组织一样适应成年以后阴茎反复勃起以及性交活动所带来的牵拉。阴茎海绵体在性生活过程中的作用与汽车的气囊在交通事故中所起的保护作用类似。
讲座 1:
| Failed hypospadias presenting in adults 2006 ESGURS Third Congress September 29 – 30, 2006 Milan – Italy |
 scarica PDF scarica PDF |
|
|
|
||
| 讲座 2: | ||
| Failed hypospadias repair presenting in adults International Congress on Hypospadias Surgery September 2-5, 2007 Prishtina – Kosova |
 scarica PDF scarica PDF |
|
|
|
||
| 讲座 3: | ||
| Hypospadias: problems in the adult patients 24th Annual EAU Congress March 17-21, 2009 Stockholm – Sweden |
 scarica PDF |
|
|
|
||
| 讲座 4: | ||
| Failed Hypospadias Repair 2nd Surgical Workshop of Complex Uro-Genital Reconstructive Surgery in Adulthood September 11-12, 2009 Belgrade – Serbia |
 scarica PDF |
|
| 讲座 5: | ||
| Problems of urethral stricture in adult male after penile and urethral reconstructive surgery in childood 41st Scientific Congress September 8 – 10, 2011 Gdańsk – Poland |
 Download PDF |
|
|
|
||
| 讲座 6: | ||
| Surgical options in adult patients with failed hypospadias repair 9th Conference of the Arab Association of Urology 7th International Conference of Jordanian Association of Urological Surgeons November 22 – 24, 2011 Amman – Jordan |
 Download PDF |
论文 1
Failed hypospadias repair presenting in adults
Eur Urol. 2006 May;49(5):887-94
论文 2
Retrospective Descriptive Analysis of 1,176 Patients With Failed Hypospadias Repair
J Urol 2010; 183: 207-211
论文 3
Surgical challenge in patients who underwent failed hypospadias repair: it is time to change?
Urol Int 2010; 85: 427-435
论文 4
Surgical Repair of Late Complications in Patients Having Undergone Primary Hypospadias Repair during Childhood: A New Perspective
Hindawi Publishing Corporation
Advances in Urology
Volume 2012, Article ID 705212, 5 pages
Failed hypospadias repair presenting in adults
Eur Urol. 2006 May;49(5):887-94
论文 2
Retrospective Descriptive Analysis of 1,176 Patients With Failed Hypospadias Repair
J Urol 2010; 183: 207-211
论文 3
Surgical challenge in patients who underwent failed hypospadias repair: it is time to change?
Urol Int 2010; 85: 427-435
论文 4
Surgical Repair of Late Complications in Patients Having Undergone Primary Hypospadias Repair during Childhood: A New Perspective
Hindawi Publishing Corporation
Advances in Urology
Volume 2012, Article ID 705212, 5 pages
1. 问: 此项手术使用什么麻醉方式?
答: 经鼻或口-气管插管的全身麻醉。
2. 问: 手术时间多长?
答: 大约2小时。
3. 问: 手术后是否有勃起功能障碍的风险?
答: 没有。
4. 问: 手术后住院时间是多长?
答: 一般来说,2到4天。
5. 问: 术后多长时间可以拔除尿管?
答: 术后尿管要保留1至2周。
6. 问: 恢复期有什么特别需要注意的问题么?
答: 在恢复期,抗生素的使用一般持续到尿管拔除以后。同时性生活暂时需要避免。
7. 问: 术后什么时候可以恢复性生活?
答: 手术后一个月后根据情况逐步恢复即可。
8. 问: 手术以后是否可以立即骑自行车或摩托车?
答: 是的。
9. 问: 术后饮食需要注意些什么?
答: 没有。
答: 经鼻或口-气管插管的全身麻醉。
2. 问: 手术时间多长?
答: 大约2小时。
3. 问: 手术后是否有勃起功能障碍的风险?
答: 没有。
4. 问: 手术后住院时间是多长?
答: 一般来说,2到4天。
5. 问: 术后多长时间可以拔除尿管?
答: 术后尿管要保留1至2周。
6. 问: 恢复期有什么特别需要注意的问题么?
答: 在恢复期,抗生素的使用一般持续到尿管拔除以后。同时性生活暂时需要避免。
7. 问: 术后什么时候可以恢复性生活?
答: 手术后一个月后根据情况逐步恢复即可。
8. 问: 手术以后是否可以立即骑自行车或摩托车?
答: 是的。
9. 问: 术后饮食需要注意些什么?
答: 没有。
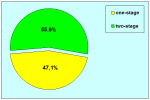
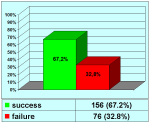
| 截止至2021年12月31日 | |||

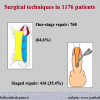
PDF One-stage |

PDF Two-stage |

总结表 |
|